Remotely debug a Python app inside a Docker container in Visual Studio Code Posted on 2018-10-22 Author Vinta Posted in Python, Web Development Visual Studio Code with Python extension has 'Remote Debugging' feature which means you could attach to a real remote host as well as a container on localhost.
- Debug containerized apps. With version 0.9.0 and later, the Docker extension provides more support for debugging applications within Docker containers, such as scaffolding launch.json configurations for attaching a debugger to applications running within a container. The Docker extension provides a docker debug configuration provider that manages how VS Code will launch an application and/or.
- In addition to snippets for authoring your Dockerfile, Visual Studio Code will provide you with a description of any Docker command you hover over with the mouse. For example, when hovering over WORKDIR you will see the following. For more information on Dockerfiles, check out Dockerfile best practices on docker.com.
- Add your user to the docker group by using a terminal to run: sudo usermod -aG docker $USER. Sign out and back in again so your changes take effect. Install Visual Studio Code or Visual Studio Code Insiders. Install the Remote Development extension pack.
- All common features of Visual Studio Code tasks (for example, grouping tasks into compound tasks) are supported by Docker extension tasks. For more information on common task features and properties, see the Visual Studio Code custom task documentation. Docker build task. The docker-build task builds Docker images using the Docker command line (CLI). The task can be used by itself, or as part of a chain of tasks to run and/or debug an application within a Docker.

Visual Studio provides a consistent way to develop Docker containers and validate your application locally.You can run and debug your apps in Linux or Windows containers running on your local Windows desktop with Docker installed, and you don't have to restart the container each time you make a code change.
This article illustrates how to use Visual Studio to start an app in a local Docker container, make changes, and then refresh the browser to see the changes. This article also shows you how to set breakpoints for debugging for containerized apps. Supported project types include .NET Framework and .NET Core web and console apps. In this article, we use ASP.NET Core web apps and .NET Framework console apps.
Visual Studio Code Docker Extension
If you already have a project of a supported type, Visual Studio can create a Dockerfile and configure your project to run in a container. See Container Tools in Visual Studio.
Prerequisites
To debug apps in a local Docker container, the following tools must be installed:
- Visual Studio 2017 with the Web Development workload installed
- Visual Studio 2019 with the Web Development workload installed
To run Docker containers locally, you must have a local Docker client. You can use Docker for Windows, which uses Hyper-V and requires Windows 10.
Docker containers are available for .NET Framework and .NET Core projects. Let's look at two examples. First, we look at a .NET Core web app. Then, we look at a .NET Framework console app.
Create a web app
If you have a project and you've added Docker support as described in the overview, skip this section.
- In the Visual Studio menu, select File > New > Project.
- In the Templates section of the New Project dialog box, select Visual C# > Web.
- Select ASP.NET Core Web Application.
- Enter a name for your new application (or use the default name), and then select OK.
- Select Web Application.
- Select the Enable Docker Support check box.
- Select the type of container you want (Windows or Linux), and then select OK.
In the Visual Studio start window, select Create a new project.
Select ASP.NET Core Web App, and then select Next.
Enter a name for your new application (or use the default name), specify the location on disk, and then select Next.
Choose the .NET version you want to target. If you don't know, choose the LTS (long-term support) release.
Choose whether you want SSL support by selecting or clearing the Configure for HTTPS check box.
Select the Enable Docker Support check box.
Select the type of container you want (Windows or Linux), and then select Create.
Edit your code and refresh
To quickly iterate changes, you can start your application in a container. Then, continue to make changes, viewing them as you would with IIS Express.
Make sure that Docker is set up to use the container type (Linux or Windows) that you are using. Right-click on the Docker icon on the Taskbar, and choose Switch to Linux containers or Switch to Windows containers as appropriate.
(.NET Core 3 and later only) Editing your code and refreshing the running site as described in this section is not enabled in the default templates in .NET Core >= 3.0. To enable it, add the NuGet package Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Razor.RuntimeCompilation. In Startup.cs, add a call to the extension method
IMvcBuilder.AddRazorRuntimeCompilationto the code in theConfigureServicesmethod. You only need this enabled in DEBUG mode, so code it as follows:Modify the
Startupmethod as follows:For more information, see Razor file compilation in ASP.NET Core.
Set Solution Configuration to Debug. Then, press Ctrl+F5 to build your Docker image and run it locally.
When the container image is built and running in a Docker container, Visual Studio launches the web app in your default browser.
Go to the Index page. We'll make changes on this page.
Return to Visual Studio and open Index.cshtml.
Add the following HTML content to the end of the file, and then save the changes.
In the output window, when the .NET build is finished and you see the following lines, switch back to your browser and refresh the page:
Your changes have been applied!
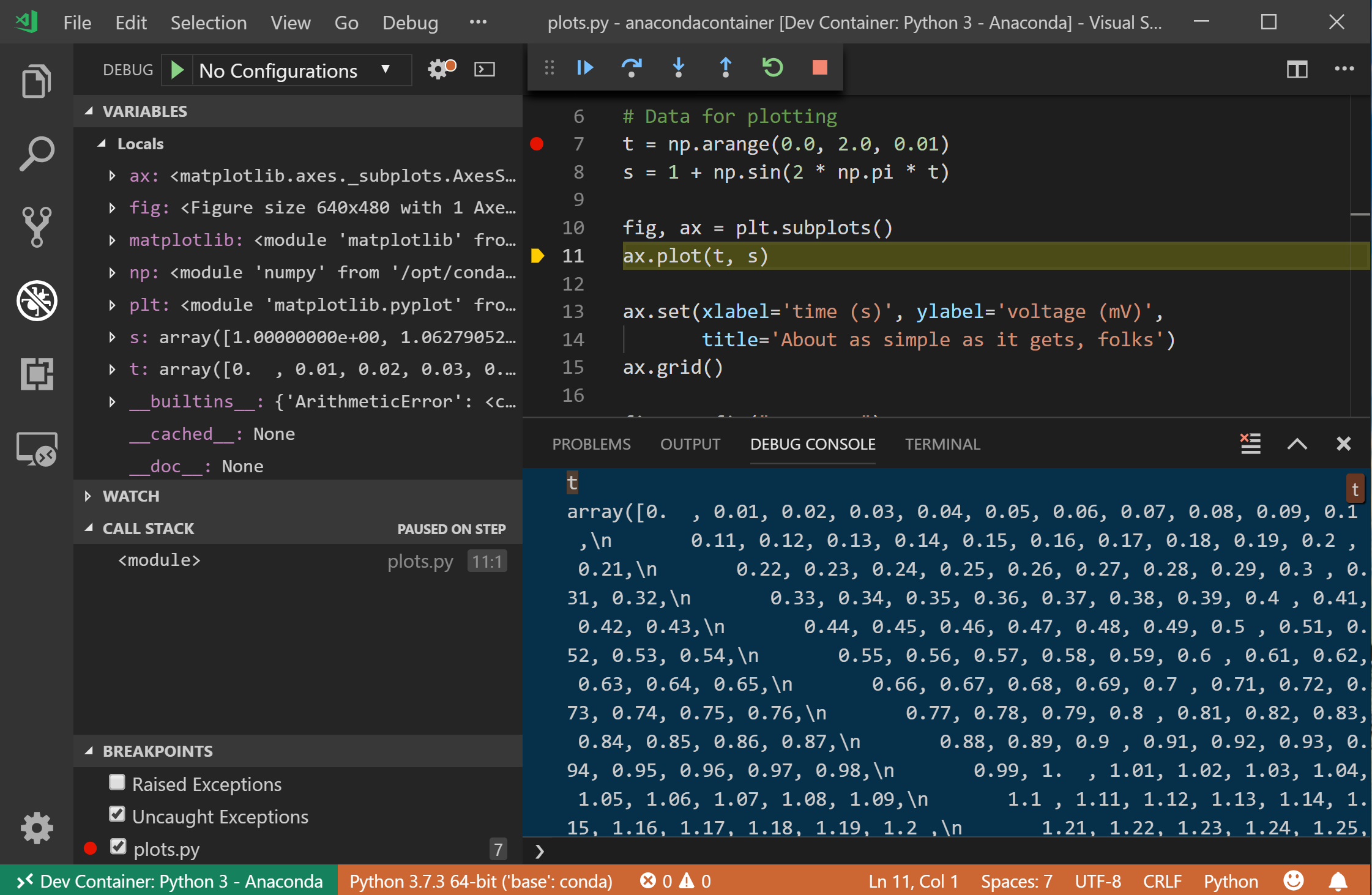
Debug with breakpoints
Often, changes require further inspection. You can use the debugging features of Visual Studio for this task.
In Visual Studio, open Index.cshtml.cs.
Replace the contents of the
OnGetmethod with the following code:To the left of the code line, set a breakpoint.
To start debugging and hit the breakpoint, press F5.
Switch to Visual Studio to view the breakpoint. Inspect values.
Create a .NET Framework console app
When you use .NET Framework console app projects, the option to add Docker support without orchestration isn't supported. You can still use the following procedure, even if you're using only a single Docker project.
- Create a new .NET Framework Console app project.
- In Solution Explorer, right-click the project node, and then select Add > Container Orchestration Support. In the dialog box that appears, select Docker Compose. A Dockerfile is added to your project and a Docker Compose project with associated support files is added.
Debug with breakpoints
In Solution Explorer, open Program.cs.
Replace the contents of the
Mainmethod with the following code:Set a breakpoint to the left of the code line.
Press F5 to start debugging and hit the breakpoint.
Switch to Visual Studio to view the breakpoint and inspect values.
Container reuse
During the development cycle, Visual Studio rebuilds only your container images and the container itself when you change the Dockerfile. If you don't change the Dockerfile, Visual Studio reuses the container from an earlier run.
If you manually modified your container and want to restart with a clean container image, use the Build > Clean command in Visual Studio, and then build as normal.
Troubleshoot
Learn how to troubleshoot Visual Studio Docker development.
Next steps
Get more details by reading How Visual Studio builds containerized apps.
More about Docker with Visual Studio, Windows, and Azure
Run Visual Studio Code In Docker Download
- Learn more about container development with Visual Studio.
- To build and deploy a Docker container, see Docker integration for Azure Pipelines.
- For an index of Windows Server and Nano Server articles, see Windows container information.
- Learn about Azure Kubernetes Service and review the Azure Kubernetes Service documentation.

